Managing Attributes in a PostGIS Dissolve
By: Bram Wiebe
Tags: GIS, Programming
For GIS programmers, PostGIS is a powerful spatial database, but the way that SQL works can cause some confusion.
When a layer is buffered and dissolved, it isn't always clear in PostGIS how to keep the attributes attached to the features they came from.
In the figure below we have six polygons, that we will assume have already been buffered. We can see that these polygons overlap in two groups:
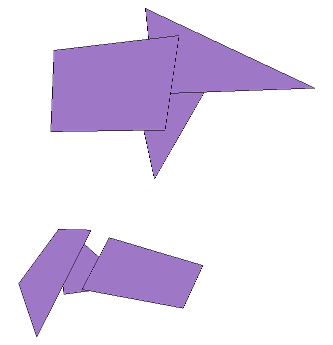
To do a spatial dissolve the ST_Union function is used as follows:
SELECT
(ST_Dump(St_multi(ST_Union(the_geom)))).geom AS the_geom
FROM
source_layer;This works but any connection to the feature attributes is lost. Trying to manage attributes in this original query is very complex and leads to unreadable and thus unmaintainable queries.
The easiest way to keep the connections between the dissolved areas and the original feature attributes is to add the connections AFTER the dissolve using ST_Intersects.
In this case we have the key field of 'id' so we will keep the lowest id for each spatial group and also keep an array list of ids that we can use for other joins later. The SQL is as follows:
SELECT
min(a.id) as id,
array_agg(a.id) as ids,
b.the_geom
FROM
source_layer a,
(SELECT
(ST_Dump(St_multi(ST_Union(the_geom)))).geom as the_geom
FROM source_layer) b
WHERE
st_intersects(a.the_geom, b.the_geom)
GROUP BY
b.the_geom;The resulting table looks like this:
| id | ids | the_geom |
| 4 | {6,5,4} | 0103... |
| 1 | {3,2,1} | 0103... |
The resulting layer looks as follows:
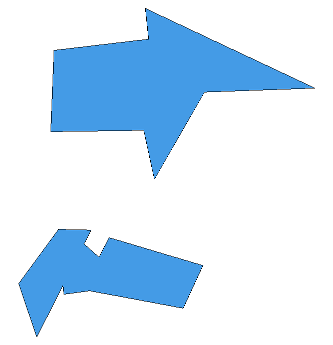
So when you want to dissolve and manage attributes in PostGIS next time, hopefully this approach will be useful to you.
